
Treating coagulopathy − Medicines or blood products may be needed if blood clotting problems become unsafe.Īcute liver failure in children is rare. It is treated by trying to prevent the production of toxic products in the liver, which cause the condition.  Treating encephalopathy – Hepatic encephalopathy always develops when liver failure is sudden and severe. The chances that the brain damage could be reversed after the transplant liver is working. Whether there is a disease in more than one organ or part of the body. The likelihood the transplant will be a success. Whether a liver transplant is advised for the child depends on: For most patients whose cause of liver failure is not known, a transplant is the only option. Transplant – About 40 percent of children with acute liver failure need a liver transplant to survive. Metabolic diseases may be treated with medicine or diet if there has not yet been any damage that cannot be reversed. Medicine may be able to reverse it if given early enough. Medicine – When the acute liver failure is caused by a cardiovascular condition, the immune system, or by acetaminophen, it can sometimes be treated with medicine. Their liver is able to reform itself into a healthy organ. Many patients whose condition is caused by a virus get better on their own. Supportive care – There are some patients who will get better on their own if they receive treatment for their symptoms. Some causes can be treated by medicine or a liver transplant. Treatment for acute liver failure depends on what caused the disease. The doctor there will figure out if the child’s cause of liver failure can be treated. If there seems to be a liver problem, the child should be seen by an expert at a liver care / transplant center. Coagulopathy (problem with blood clotting). Levels of liver enzymes that increase very quickly. Signs of mental confusion (encephalopathy). Lab studies and a physical exam can tell if there are signs of a liver problem. Older children may seem angry, have a hard time falling asleep, forget things, be confused, or feel drowsy. Infants older than 28 days may be irritable, have crying spells and can't be made to feel better, or they might want to sleep more during the day than at night. Infants up to 28 days old may not have many signs of encephalopathy that are easy to notice. A liver that is working like it should is able to break down toxins and carry them out of the liver.
Treating encephalopathy – Hepatic encephalopathy always develops when liver failure is sudden and severe. The chances that the brain damage could be reversed after the transplant liver is working. Whether there is a disease in more than one organ or part of the body. The likelihood the transplant will be a success. Whether a liver transplant is advised for the child depends on: For most patients whose cause of liver failure is not known, a transplant is the only option. Transplant – About 40 percent of children with acute liver failure need a liver transplant to survive. Metabolic diseases may be treated with medicine or diet if there has not yet been any damage that cannot be reversed. Medicine may be able to reverse it if given early enough. Medicine – When the acute liver failure is caused by a cardiovascular condition, the immune system, or by acetaminophen, it can sometimes be treated with medicine. Their liver is able to reform itself into a healthy organ. Many patients whose condition is caused by a virus get better on their own. Supportive care – There are some patients who will get better on their own if they receive treatment for their symptoms. Some causes can be treated by medicine or a liver transplant. Treatment for acute liver failure depends on what caused the disease. The doctor there will figure out if the child’s cause of liver failure can be treated. If there seems to be a liver problem, the child should be seen by an expert at a liver care / transplant center. Coagulopathy (problem with blood clotting). Levels of liver enzymes that increase very quickly. Signs of mental confusion (encephalopathy). Lab studies and a physical exam can tell if there are signs of a liver problem. Older children may seem angry, have a hard time falling asleep, forget things, be confused, or feel drowsy. Infants older than 28 days may be irritable, have crying spells and can't be made to feel better, or they might want to sleep more during the day than at night. Infants up to 28 days old may not have many signs of encephalopathy that are easy to notice. A liver that is working like it should is able to break down toxins and carry them out of the liver. 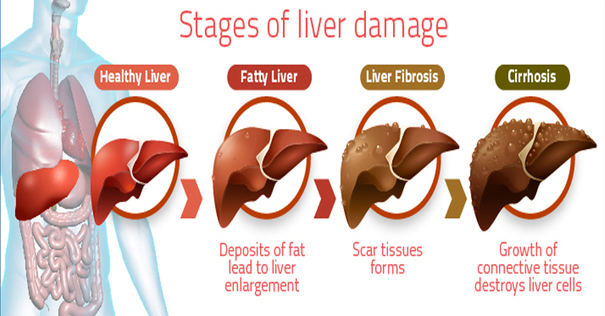
This happens when the liver is not able to break down or get rid of toxic products. In encephalopathy the brain does not work the way it should. This can quickly progress to jaundice (yellowing of the skin), encephalopathy and coagulopathy (problem with blood clotting). This can include upset stomach, feeling tired all the time, or throwing up.
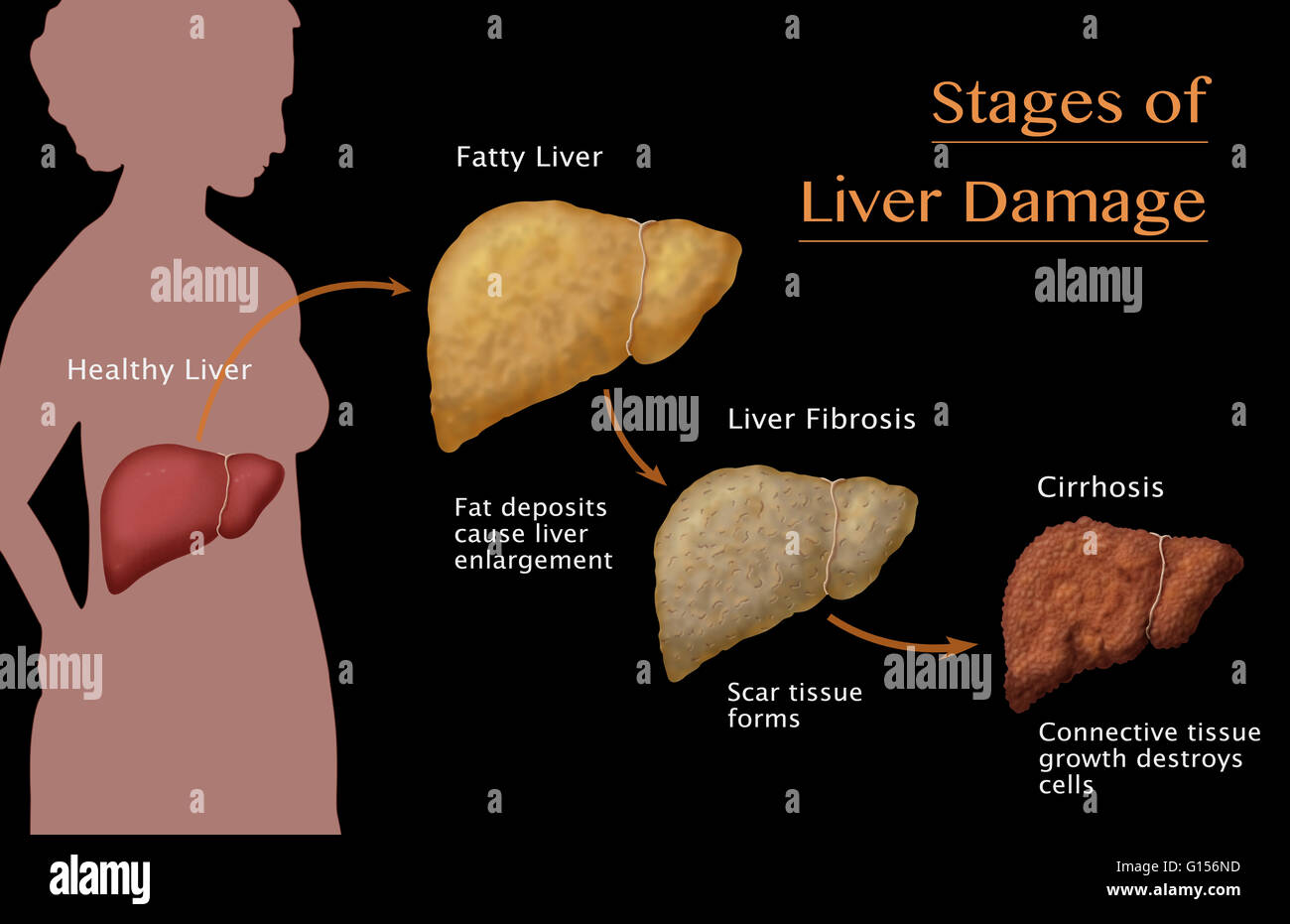
Symptoms of acute liver failure can be like those of a virus. Signs and Symptoms of Acute Liver Failure
Metabolic: Fatty acid oxidation, Reye's syndrome, leukemia, others. Cardiovascular: Myocarditis, heart surgery, cardiomyopathy, Budd-Chiari syndrome. Drugs / toxins: Valproic acid, isoniazid, halothane, acetaminophen, mushroom, phosphorous, aspirin, others. Infections: Hepatitis A, B and D, NANB hepatitis, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, herpes, leptospirosis, others. Immune: Autoimmune hepatitis, immune dysregulation, immune deficiency, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Metabolic: Galactosemia, tyrosinemia, iron storage, mitochondrial condition, HFI, fatty acid oxidation, others. Cardiovascular: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, hypoplastic left heart syndrome, shock, asphyxia, myocarditis. Infections: Herpes simplex, echovirus, adenovirus, hepatitis B, parvovirus, others. This number is about 63 percent in children with acute liver failure under 2 years of age. One study showed that this was the case for about 44 percent of all children with acute liver failure. Often the cause of acute liver failure in children cannot be found. 
Cardiovascular conditions (which cause a lack of blood supply to the liver).Metabolic conditions (problems with the physical and chemical processes inside the liver that must happen for a person to live).This can happen if a child is given the wrong dose of medicine or if too much is taken in a short amount of time. Acetaminophen (such as Tylenol®) is one common medicine that can affect how the liver works.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
